Thermal-Resistance Ratings: U-factor vs. R-value
U-factor and R-value measure heat transfer and heat resistance, respectively; understanding the difference will help you select energy-efficient windows and insulation.

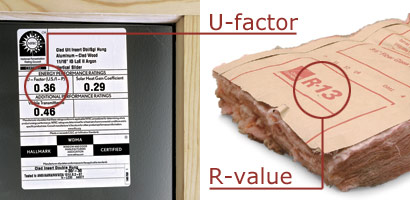
Both U-factor and R-value are measures of a material’s insulating performance. The former is a measurement of heat transfer; the latter measures heat resistance.
U-factor
Generally used to compare the performance of windows, U-factor first was invented by engineers and scientists as a measure of the rate at which heat flows through 1 sq. ft. of material. The direct opposite of an R-value, a lower U-factor rating means that less heat will be lost.
U-factor ratings generally fall between 0.20 and 1.20. A window that has a U-factor of 0.40 or less is considered energy efficient.
R-value
Created as a way to sell insulation, R-value is a measure of resistance to heat flow. The higher the number, the greater the insulating value.
Because doubling the R-value cuts heat loss in half, adding R-1 to R-1 will make a big difference; but adding R-1 to R-30 will reduce heat loss by only about 3%.
A good installation technique is the key to getting a good R-value. For instance, R-19 insulation installed incorrectly probably will perform at a level of R-13.
Bruce Harley is the author of Build Like a Pro: Insulate and Weatherize, published by The Taunton Press.
Fine Homebuilding Recommended Products
Fine Homebuilding receives a commission for items purchased through links on this site, including Amazon Associates and other affiliate advertising programs.

Homebody: A Guide to Creating Spaces You Never Want to Leave

Utility Knife

Caulking Gun

























