These Technologies Will Move Renewable Energy Forward
New battery types and advanced renewable fuels are on the horizon.

by Kerry Rippy
In recent decades the cost of wind and solar power generation has dropped dramatically. This is one reason that the U.S. Department of Energy projects that renewable energy will be the fastest-growing U.S. energy source through 2050.
However, it’s still relatively expensive to store energy. And since renewable energy generation isn’t available all the time—it happens when the wind blows or the sun shines—storage is essential.
As a researcher at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), I work with the federal government and private industry to develop renewable energy storage technologies. In a recent report, researchers at NREL estimated that the potential exists to increase U.S. renewable energy storage capacity by as much as 3000% percent by 2050.
Here are three emerging technologies that could help make this happen.
Longer charges
From alkaline batteries for small electronics to lithium-ion batteries for cars and laptops, most people already use batteries in many aspects of their daily lives. But there is still lots of room for growth.
For example, high-capacity batteries with long discharge times—up to 10 hours—could be valuable for storing solar power at night or increasing the range of electric vehicles. Right now there are very few such batteries in use. However, according to recent projections, upwards of 100 gigawatts’ worth of these batteries will likely be installed by 2050. For comparison, that’s 50 times the generating capacity of Hoover Dam. This could have a major impact on the viability of renewable energy.
One of the biggest obstacles is limited supplies of lithium and cobalt, which currently are essential for making lightweight, powerful batteries. According to some estimates, around 10% of the world’s lithium and nearly all of the world’s cobalt reserves will be depleted by 2050.
Furthermore, nearly 70% of the world’s cobalt is mined in the Congo, under conditions that have long been documented as inhumane.
Scientists are working to develop techniques for recycling lithium and cobalt batteries, and to design batteries based on other materials. Tesla plans to produce cobalt-free batteries within the next few years. Others aim to replace lithium with sodium, which has properties very similar to lithium’s but is much more abundant.
Safer batteries
Another priority is to make batteries safer. One area for improvement is electrolytes—the medium, often liquid, that allows an electric charge to flow from the battery’s anode, or negative terminal, to the cathode, or positive terminal.
When a battery is in use, charged particles in the electrolyte move around to balance out the charge of the electricity flowing out of the battery. Electrolytes often contain flammable materials. If they leak, the battery can overheat and catch fire or melt.
Scientists are developing solid electrolytes, which would make batteries more robust. It is much harder for particles to move around through solids than through liquids, but encouraging lab-scale results suggest that these batteries could be ready for use in electric vehicles in the coming years, with target dates for commercialization as early as 2026.
While solid-state batteries would be well suited for consumer electronics and electric vehicles, for large-scale energy storage, scientists are pursuing all-liquid designs called flow batteries.
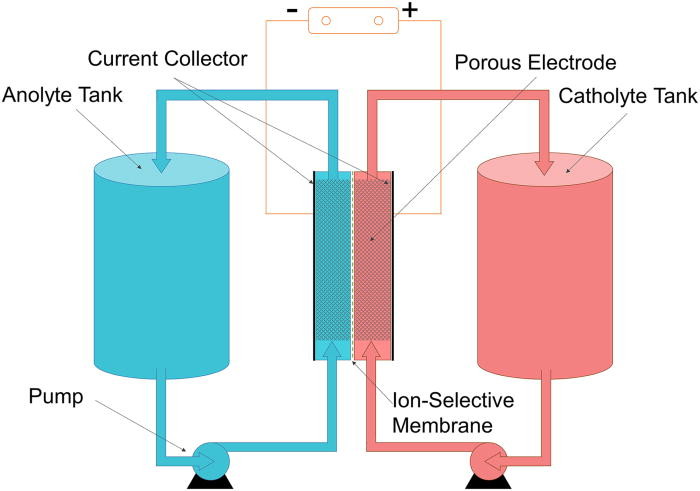
In these devices both the electrolyte and the electrodes are liquids. This allows for super-fast charging and makes it easy to make really big batteries. Currently these systems are very expensive, but research continues to bring down the price.
Storing sunlight as heat
Other renewable energy storage solutions cost less than batteries in some cases. For example, concentrated solar power plants use mirrors to concentrate sunlight, which heats up hundreds or thousands of tons of salt until it melts. This molten salt is used to drive an electric generator, much as coal or nuclear power is used to heat steam and drive a generator in traditional plants.
These heated materials can also be stored to produce electricity when it is cloudy, or even at night. This approach allows concentrated solar power to work around the clock.

This idea could be adapted for use with nonsolar power generation technologies. For example, electricity made with wind power could be used to heat salt for use later when it isn’t windy.
Concentrating solar power is still relatively expensive. To compete with other forms of energy generation and storage, it needs to become more efficient. One way to achieve this is to increase the temperature the salt is heated to, enabling more efficient electricity production. Unfortunately, the salts currently in use aren’t stable at high temperatures. Researchers are working to develop new salts or other materials that can withstand temperatures as high as 1300°F (705°C).
One leading idea for how to reach higher temperature involves heating up sand instead of salt, which can withstand the higher temperature. The sand would then be moved with conveyor belts from the heating point to storage. The Department of Energy recently announced funding for a pilot concentrated solar power plant based on this concept.
Advanced renewable fuels
Batteries are useful for short-term energy storage, and concentrated solar power plants could help stabilize the electric grid. However, utilities also need to store a lot of energy for indefinite amounts of time. This is a role for renewable fuels like hydrogen and ammonia. Utilities would store energy in these fuels by producing them with surplus power, when wind turbines and solar panels are generating more electricity than the utilities’ customers need.
Hydrogen and ammonia contain more energy per pound than batteries, so they work where batteries don’t. For example, they could be used for shipping heavy loads and running heavy equipment, and for rocket fuel.
Today these fuels are mostly made from natural gas or other nonrenewable fossil fuels via extremely inefficient reactions. While we think of it as a green fuel, most hydrogen gas today is made from natural gas.
Scientists are looking for ways to produce hydrogen and other fuels using renewable electricity. For example, it is possible to make hydrogen fuel by splitting water molecules using electricity. The key challenge is optimizing the process to make it efficient and economical. The potential payoff is enormous: inexhaustible, completely renewable energy.
Previously published on GreenBuildingAdvisor.com. Kerry Rippy is a researcher at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Golden, Colorado. This post was originally published at The Conversation and is republished here under a Create Commons license.





