
Fine Homebuilding Project Guides
Insulation
Trusted, comprehensive guidance from the pros for a home that is healthy, comfortable, and energy efficient
If the word insulation conjures up images of rolling out fiberglass batts in a hot, cramped attic and little else, think again. While installing insulation is certainly one thing you'll learn about in this comprehensive project guide, there's a lot more to it than that. An introductory chapter on energy efficiency presents some key concepts that will help you understand how to make your home healthier, more comfortable, and more energy efficient. Before you insulate your home, however, you need to make it more airtight, the subject of the second chapter. At the heart of this guide, two chapters provide valuable information on how to choose and install insulation. The final chapter looks at the role of water-resistive barriers in ensuring a high-performance home, because, let's face it, if you're not keeping water out, nothing else matters.
Choose a Chapter
Search Guide-
Energy Efficiency
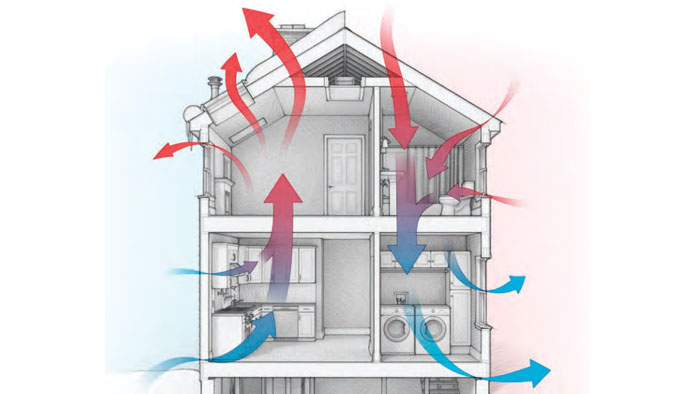
Insulation is one of the cornerstones of an energy-efficient house, but it's important that we understand its role withing the broader context of some basic energy concepts. This introductory chapter provides a crash course in such topics as the stack effect, thermal bridging, and what we mean by vapor barriers and other control layers. Also included are some examples of specific types of high-performance homes, including net zero, passive house, and the aptly named "pretty good house"—a house that strikes a balance between construction cost and energy performance.
-
Air-Sealing

As should be clear by now, before you insulate your home you need to make it airtight. Air-sealing not only keeps conditioned air inside the house, but it also improves the performance of insulation by stopping air from moving through it. In addition, air-sealing reduces the possibility of condensation developing in building cavities, which can lead to mold and decay. This chapter features information on tools and materials for air-sealing, including the all-important blower door test. You'll also learn how to air-seal all the parts of the house, from the foundation to the attic.
-
Choosing Insulation

There are more different types of insulation than there are climate zones, and in this chapter we'll assess the pros and cons of the most common types to help you choose the appropriate insulation for your home. It's hard to pick one "best" type of insulation as there are many variables to consider—and not just R-value. Fiberglass is still the number one choice for home insulation, but other options include rigid foam and spray foam, blown-in cellulose, mineral wool, cotton batts, wood fiber, and three materials with attractive environmental credentials: straw, hemp, and cork.
-
Installing Insulation

Now that you know about the various insulation options, it's finally time for the installation. This chapter starts at the top of the house and works its way down from the roof to the foundation. Along the way, you'll learn how to insulate the attic with blown-in cellulose, use rigid exterior foam to insulate the walls, install a superinsulated slab foundation, insulate your basement walls with closed-cell spray foam, and much more. And, yes, we'll give you some tips about working with fiberglass batts, too.
-
Water Management
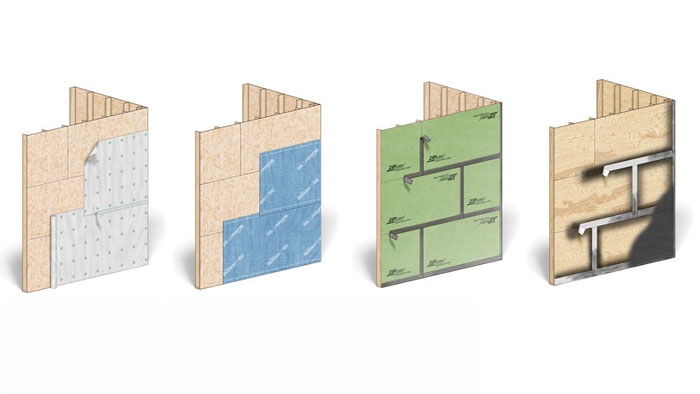
Along with air-sealing and insulation, water management is a critical third component of a high-performance home. You not only need to manage air and temperature to build a home that is comfortable and durable, but also water and vapor. Enter the water-resistive barrier, a.k.a. WRB, whose primary role is to keep water from getting into the walls of the house. This chapter will present some of the most well-known types of WRBs as well as some of the newer products to come to market. And in the final section, you'll learn how to install some of these water-resistive barriers.
- Home Group
- Antique Trader
- Arts & Crafts Homes
- Bank Note Reporter
- Cabin Life
- Cuisine at Home
- Fine Gardening
- Fine Woodworking
- Green Building Advisor
- Garden Gate
- Horticulture
- Keep Craft Alive
- Log Home Living
- Military Trader/Vehicles
- Numismatic News
- Numismaster
- Old Cars Weekly
- Old House Journal
- Period Homes
- Popular Woodworking
- Script
- ShopNotes
- Sports Collectors Digest
- Threads
- Timber Home Living
- Traditional Building
- Woodsmith
- World Coin News
- Writer's Digest




